The worldwide logistics sector is experiencing a pivotal transformation driven by Electric Vehicle Finance solutions. With online retail expanding rapidly and metropolitan areas enforcing stricter environmental standards, electric-powered transportation—especially delivery bikes and last-mile logistics vehicles—has become indispensable for eco-conscious business operations. The electric cargo bike market valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2023 demonstrates this shift, with forecasts indicating 10% annual growth through 2030, ultimately reaching USD 4.09 billion. For logistics companies pursuing sustainable futures, understanding Electric Vehicle Finance options and the financial frameworks supporting this evolution proves essential.
Electric Delivery Solutions Experience Remarkable Expansion
Commercial delivery operations have transformed substantially, influenced by environmental mandates, cost pressures, and evolving customer demands. Market analysts project the global electric cargo bike sector will surge from USD 4.78 billion in 2025 to USD 18.05 billion by 2035, representing 14.2% compound annual growth—driven primarily by urgent requirements to eliminate carbon from final-mile logistics while reducing metropolitan traffic density.
Source: Global Market Insight
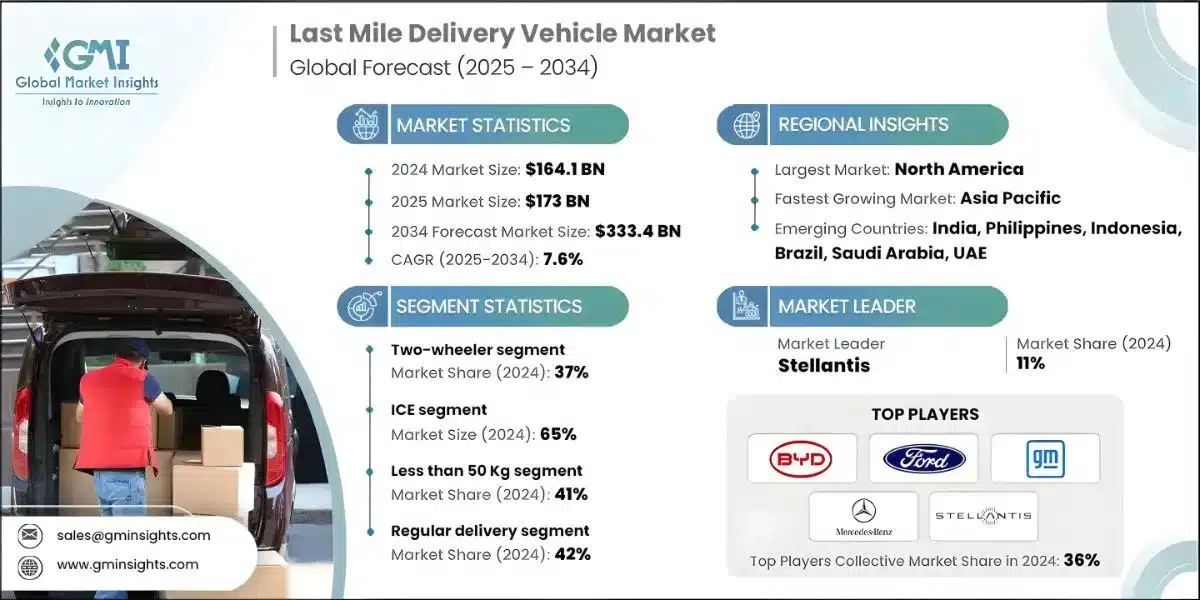
Within the last-mile delivery sphere specifically, the market surpassed USD 164.1 billion in 2024, with projections showing 7.6% yearly expansion through 2034. This trajectory fundamentally alters how products navigate urban environments.
Cargo Bikes Transform Urban Delivery
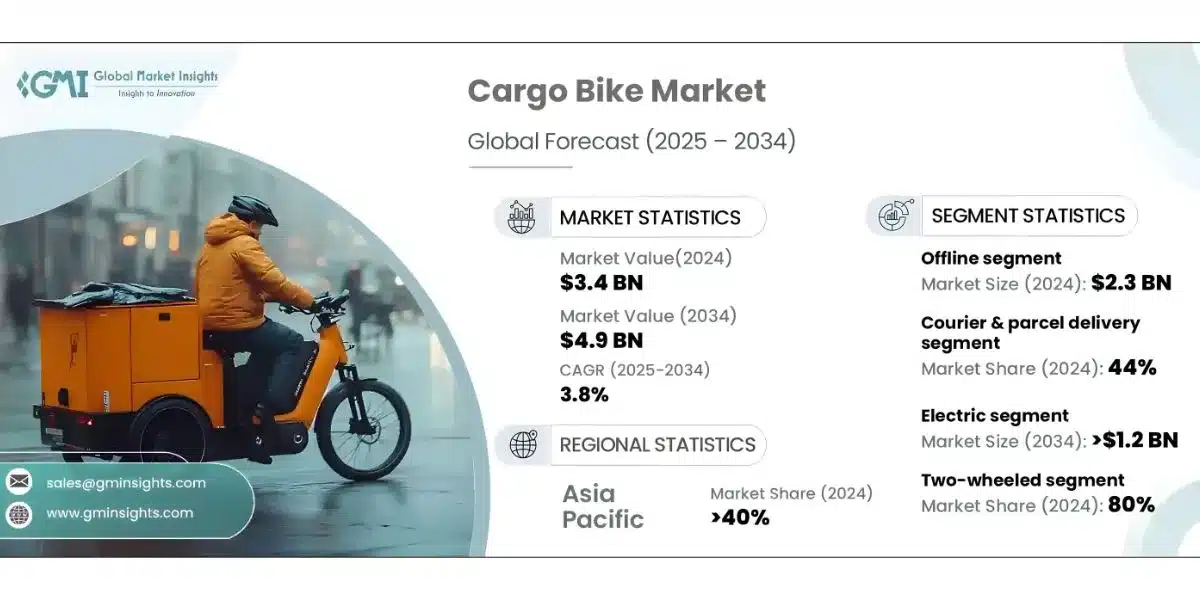
Electric cargo bicycles have evolved from specialized equipment to fundamental logistics infrastructure. Industry data shows the global cargo bike market was valued at USD 3.4 billion in 2024, projected to expand 3.8% annually between 2025 and 2034, with courier services leading implementation. Significantly, package delivery operations commanded 44% of total market activity in 2024.
Leading logistics enterprises have wholeheartedly adopted this innovation. During March 2022, Ocado introduced electric cargo bikes throughout London’s delivery network, deploying units capable of transporting 120+ kg loads while maintaining refrigeration. Such implementations showcase how cargo bikes have progressed beyond pilot programs into mission-critical assets.
Market research indicates the three-wheeled configuration will achieve the most rapid growth, anticipated to reach 15.6% CAGR from 2025 through 2035, thanks to enhanced stability, greater load capabilities, and flexible commercial applications. These designs particularly excel in demanding operations including municipal services and high-volume parcel distribution within city centers.
Electrification Accelerates Across Last-Mile Operations
Source: Grand View research
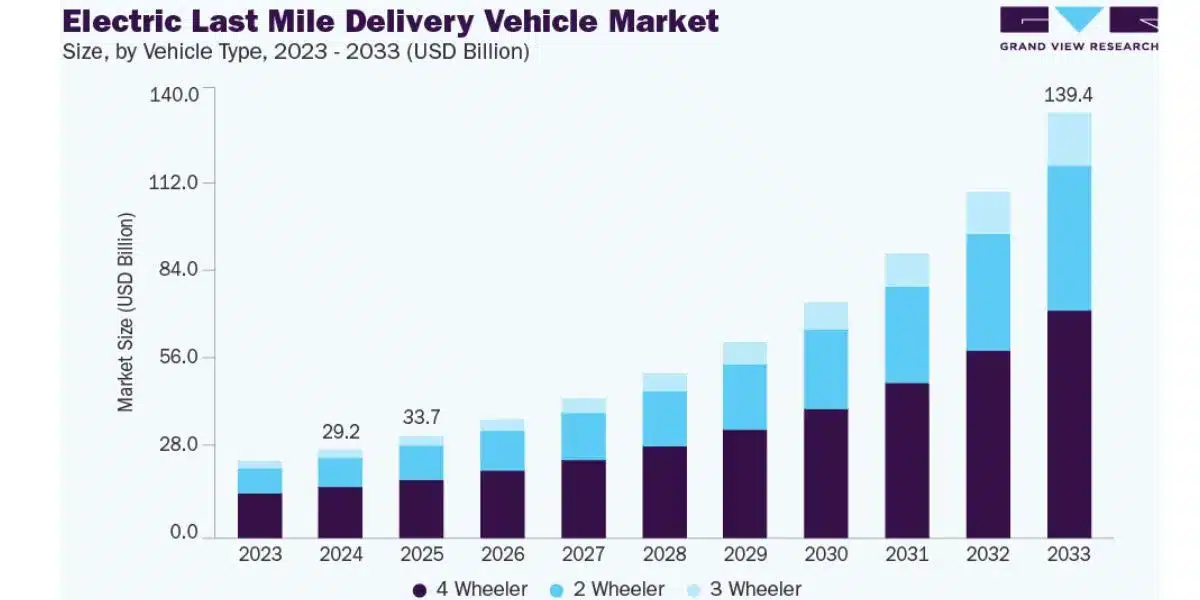
Extending beyond cargo bicycles, the comprehensive electric final-mile delivery vehicle sector demonstrates explosive momentum. Data reveals the global electric last-mile delivery van market size reached USD 6.8 billion in 2024, with forecasts projecting 14.2% annual growth from 2025 to 2033, ultimately attaining USD 22.3 billion by 2033.
Vehicle category analysis exposes operational priorities: Two-wheel configurations captured approximately 37% market share in 2024, projected to expand 6.8% yearly through 2034, with micro-mobility solutions including e-bikes and cargo cycles exhibiting the strongest growth trajectory.
Financial Frameworks Enabling Logistics Transformation
Total Ownership Economics Reveal Compelling Advantages
Despite elevated initial acquisition costs, comprehensive financial modeling demonstrates significant long-term benefits:
Energy Cost Benefits: Research confirms electricity expenses register 80% below diesel on per-mile basis, generating immediate operational gains. High-frequency urban delivery routes experience particularly notable savings.
Maintenance Expense Reductions: Electric delivery platforms require substantially diminished upkeep. Eliminating oil changes, featuring fewer mechanical components, and utilizing regenerative braking systems enable operators to achieve maintenance expenditure decreases of 40-50% versus conventional delivery vehicles.
Documented Fleet Economics: Comprehensive assessment of 270 light-duty vehicles demonstrated 30% greenhouse gas reduction potential alongside $1.3 million cost savings throughout fleet lifetime. Extended analysis revealed 13.7% per-fleet savings, $4.85 million total ownership cost reductions, and 1,200 metric tons of CO2 elimination across 1,237 vehicles.
Final-Mile Financial Reality: Industry analysis confirms last-mile delivery consumes 53% of complete shipping expenditures, making efficiency enhancements within this segment exceptionally valuable. Electric vehicles’ capability to traverse congested metropolitan zones, enter pedestrian areas, and bypass low-emission charges generates immediate competitive benefits.
Government Programs and Infrastructure Backing
Public sector support mechanisms remain vital catalysts for electric delivery fleet implementation:
United States Initiatives:
- U.S. Inflation Reduction Act provisions: Maximum $40,000 commercial EV tax credits
- Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit: Maximum $100,000 per charging installation
- Complementary state and municipal programs that combine with federal support
European Programs:
- EU’s Green Deal framework: Prohibits new fossil-fuel vans after 2035 while funding charging stations
- Low-emission district access exemptions throughout major metropolitan areas
- City-level cargo bike infrastructure development
Asia-Pacific Mechanisms:
- India’s FAME-II Scheme: Subsidies offsetting 40% of fleet EV expenditures
- China’s comprehensive EV subsidization and charging network investments
- Regional support frameworks across Southeast Asia
Multiple Financing Pathways for Logistics Companies
Commercial logistics organizations can utilize various financing approaches customized for delivery applications:
- Equipment Leasing Arrangements: Enable deployment of electric cargo bikes and delivery platforms without substantial capital requirements, featuring tax-deductible payment structures
- Specialized Fleet Financing: Purpose-built loans for electric vehicle fleets offering advantageous terms reflecting total ownership economics
- Subscription-Based Access: Emerging platforms allowing delivery enterprises to utilize electric vehicles through pay-per-use models
- Sustainability-Linked Financial Products: Expanding availability of preferential financing connected to environmental performance indicators
- Battery-as-a-Service Solutions: Separates energy storage costs from vehicle purchase, diminishing initial investment while guaranteeing battery performance
Environmental Performance: Measuring Sustainability Outcomes
Urban Logistics Emission Reductions
The sustainability argument for electric delivery platforms receives validation through extensive commercial deployment data:
Metropolitan Air Quality: Electric cargo bikes and delivery vehicles generate zero tailpipe pollution, directly improving urban atmospheric conditions. This assumes particular significance considering the International Energy Agency identifies transport as responsible for 24% of global CO₂ emissions, with logistics contributing substantially.
Corporate Environmental Pledges: Current data indicates 73% of Fortune 500 enterprises maintain formal carbon reduction commitments, accelerating aggressive fleet electrification strategies. Industry-leading logistics providers spearhead this movement:
- UPS operates 12,000+ electric and hybrid vehicles throughout its global network pursuing carbon neutrality by 2050
- Amazon currently deploys 20,000 electric delivery vehicles advancing toward its 100,000-vehicle objective by 2030
- Zypp Electric collaborates with Zomato in India deploying 100,000 e-scooters targeting 35 million kg carbon emission reductions by 2024
Quantified Environmental Impact: Fleet analysis documents fuel consumption decreases reaching 536,000 liters across 1,237 vehicles, illustrating the environmental benefit magnitude achievable through systematic electrification.
Regulatory Adherence and Urban Accessibility
Metropolitan governments worldwide implement progressively restrictive emission policies fundamentally transforming delivery economics:
Low-Emission District Requirements: Netherlands data reveals how low-emission zone implementation from 2025 propelled electric LCV sales share beyond 90% during 2025’s first quarter, contrasting sharply with the prior year’s sub-10% average.
Preferential Access Rights: Municipal low-emission districts increasingly prohibit diesel vans from dense commercial cores, compelling fleet operators toward e-cargo solutions avoiding congestion fees while satisfying Scope 3 reporting requirements.
Operational Performance Benefits: Fleet managers report e-cargo units completing peak-hour routes faster than traditional light vans, simultaneously reducing parking violations and congestion charges. Electric cargo bikes’ pedestrian zone access and narrow street navigation provide competitive advantages unattainable with conventional delivery platforms.
Strategic Deployment for Logistics Operations
Vehicle Selection and Fleet Configuration
Effective electric delivery fleet implementation demands strategic vehicle choices:
Cargo Bike Options:
- Two-wheel configurations priced $1,000-$3,000 provide affordability and maneuverability
- Three-wheel platforms deliver enhanced stability for heavy loads, commanding premium pricing reflecting added engineering
- Electric cargo bikes incorporate pedal-assist motors optimizing heavy load transport across extended distances, typically priced $2,500-$8,000
Application-Optimized Deployment: Market projections show the courier & parcel services segment achieving fastest expansion at 15.4% CAGR from 2025 through 2035, propelled by e-commerce growth and demand for efficient, environmentally-responsible final-mile solutions.
Fleet composition analysis indicates the 4-wheeler category commanded 57.28% market dominance in 2024 reflecting superior payload capacity, extended operational range, and appropriateness for structured high-volume delivery operations, while 3-wheeler configurations emerge as flexible hyperlocal delivery solutions featuring minimal upfront and operating expenditures.
Technology Integration and Route Enhancement
Contemporary electric delivery fleets leverage advanced technological integration:
AI-Driven Optimization: AI implementation in cargo bikes facilitates intelligent route planning utilizing real-time traffic data, decreasing delivery duration and logistics operator expenses. AI-powered fleet management platforms monitor performance metrics, battery conditions, and maintenance requirements ensuring maximum operational availability.
Telematics Platforms: Advanced fleet management solutions deliver real-time operational visibility encompassing vehicle positioning, battery status, route effectiveness, and driver performance. These data streams enable continuous delivery operation optimization.
Intelligent Charging Systems: Smart load distribution staggers charging schedules, capitalizes on reduced tariffs, and provides dispatch alerts during grid demand surges, preventing expensive power consumption penalties.
Infrastructure and Energy Solutions
Strategic charging infrastructure planning proves essential for successful fleet electrification:
Depot-Based Charging: Overnight facility charging exploits off-peak electricity pricing, delivering the most economical charging approach for predictable route patterns.
Battery Exchange Systems: Emerging throughout high-density markets, battery swapping facilities enable immediate vehicle turnaround, eliminating charging delays for time-critical operations.
Public Rapid Charging: BP Pulse & Shell Recharge establish high-speed charging depots specifically for logistics fleets, supplementing depot infrastructure for extended-range applications.
Renewable Energy Integration: On-site solar installations reduce electricity expenditures while further diminishing electric logistics operations’ carbon intensity.
Sustained Value Generation for Logistics Providers
Operational Performance Improvements
Beyond direct expenditure reductions, electric delivery fleets unlock numerous operational benefits:
Expanded Service Windows: Electric vehicles’ silent operation permits deliveries during extended timeframes within noise-restricted districts, enhancing operational flexibility.
Minimized Downtime: Granular stop-level analytics matches compact vans with concentrated postal circuits while reserving larger e-trucks for pallet operations, protecting range and payload parameters, optimizing fleet utilization.
Superior Driver Experience: Electric vehicles provide smoother operations, instantaneous torque for stop-and-go delivery patterns, and enhanced cabin comfort, supporting driver satisfaction and workforce retention.
Brand Distinction and Customer Engagement
Sustainability credentials increasingly shape consumer purchasing decisions and business relationships:
Consumer Alignment: Growing demand for sustainable delivery options creates competitive advantages for electric fleet operators.
Enterprise Collaborations: IKEA pledged 100% zero-emission final-mile deliveries across major metropolitan centers including New York, Paris, Shanghai, and London, utilizing electric vans, e-cargo bikes, and even electric watercraft regionally.
ESG Advancement: Numerous major corporations and logistics providers synchronize operations with ESG objectives, pursuing carbon neutrality throughout supply chains.
Geographic Market Patterns and Expansion
Regional Implementation Trends
Electric logistics vehicle adoption varies considerably across regions, influenced by local regulations, infrastructure availability, and market dynamics:
Asia-Pacific Dominance: Asia-Pacific commanded 48.14% revenue in 2024 within the e-cargo bike sector, led by China’s extensive EV incentivization and accelerated urbanization. China secures substantial market presence in the cargo bike industry reflecting supportive governmental frameworks and rapid urban development.
North American Momentum: North America represents the fastest expanding region at 7.30% CAGR to 2030. North America achieved approximately USD 2.1 billion market valuation in 2024, with regional projections indicating 13.8% growth through 2033.
European Market Leadership: North America and Europe collectively command over 70% of global sales reflecting established infrastructure and governmental incentivization. Europe’s widespread low-emission districts and urban delivery constraints drive particularly robust cargo bike implementation.
Developing Market Possibilities
While Brazil and Poland experience rapid acceleration reflecting urban densification and regulatory support, established markets like Japan demonstrate modest expansion due to spatial limitations. This generates distinct opportunities for customized financial solutions across varied markets.
Navigating Implementation Obstacles
Resolving Range and Capacity Constraints
Modern electric delivery vehicles increasingly address conventional limitations:
Energy Storage Innovation: February 2024 saw Tern announce its electric cargo expansion launching the Orox, featuring 1,600Wh battery capacity, supporting 210 kg maximum loads, and promising 300+ km operational range.
Route Analysis: Telematics information frequently demonstrates most urban circuits comfortably operate within 120-mile battery parameters, rendering range concerns largely unfounded for typical last-mile delivery applications.
Capital Requirement Management
Leasing Structures: Leasing arrangements, residual-value assurances, and energy savings compress breakeven timeframes below standard asset lifecycles, enabling electrification without substantial capital commitments.
Incremental Implementation: Phased-deployment methodologies organize routes by distance, terrain, and charger accessibility, ensuring each new van enters operation on precisely appropriate circuits, minimizing risk while developing operational expertise.
Future Trajectory
The convergence of declining vehicle expenditures, advancing battery technology, expanding charging infrastructure, and compelling financial incentivization creates extraordinary logistics electrification opportunities. As enterprises increasingly adopt electric vehicles for last-mile delivery reflecting green supply chain initiatives and competitive sustainability positioning, this transition yields beneficial effects societally and commercially.
Major corporate commitments indicate industry direction:
- Walmart committed to acquiring 4,500 all-electric delivery vehicles
- Domino’s purchasing 800 Chevy Bolt electric vehicles for U.S. store deployment
- Amazon launched comprehensive last-mile fleet initiative in India, introducing entirely electric fleets supporting 300+ Delivery Service Partners
The logistics sector’s electric transformation transcends “whether” to focus on “when” and “how.” Organizations strategically leveraging available financing mechanisms, investing in appropriate charging infrastructure, and implementing data-driven deployment strategies position themselves for sustained competitive advantage within increasingly carbon-conscious marketplaces.
Electric vehicles prove especially suitable for last-mile delivery operations given fixed and constrained operational ranges—establishing urban logistics as the optimal commercial electrification entry point. For logistics operators, the question centers not on whether to electrify, but rather how rapidly and strategically they can execute this transition capturing maximum financial and environmental returns while satisfying escalating expectations from customers, regulators, and stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the typical ROI timeline for electric cargo bikes and delivery vehicles in commercial logistics?
Most logistics operators achieve positive ROI within 2-5 years, with high-utilization urban fleets often seeing payback in 18-36 months. Key factors driving faster returns include 80% lower electricity costs versus diesel, 40-50% reduced maintenance expenses, and government incentives up to $40,000 per commercial EV. Urban delivery operations with predictable routes become cost-positive almost immediately when factoring in avoided congestion charges and low-emission zone benefits.
2. How do financing options for electric delivery fleets differ from traditional commercial vehicle financing?
Electric delivery vehicle financing offers several advantages: lower interest rates through green lending programs, flexible payment structures aligned with fuel savings, battery-as-a-service options reducing upfront costs, integrated charging infrastructure packages, and residual value guarantees. Many specialized EV fleet programs allow businesses to capture tax credits immediately, while leasing arrangements often bundle maintenance, software, and charging services into comprehensive operational solutions.
3. What are the main operational challenges when transitioning to electric delivery vehicles, and how can they be mitigated?
The three primary challenges and solutions are:
Range Management: Most urban delivery routes operate within 120-mile battery limits. Mitigate through route profiling, strategic fast-charging placement, battery swapping stations, and phased deployment starting with shorter routes.
Infrastructure Costs: Minimize through depot overnight charging at off-peak rates, government grants (up to $100,000 per charging port), smart load management, and partnerships with charging infrastructure providers.
Fleet Optimization: Conduct detailed route analysis to match vehicle types appropriately—cargo bikes for dense urban areas, light vans for suburbs, larger trucks for consolidated deliveries. Start with pilot programs to build expertise before full-scale deployment.